Varieties Of The Dorsal Artery Of The Penis
Description
This section is from the book "Anatomy Of The Arteries Of The Human Body", by John Hatch Power. Also available from Amazon: Anatomy of the Arteries of the Human Body, with the Descriptive Anatomy of the Heart.
Varieties Of The Dorsal Artery Of The Penis
This artery sometimes comes directly from the iliac, and passes along the side of the prostate gland, to arrive at its destination. The late Dr. M'Dowel remarked that this variety was more frequent on the left than on the right side.
Dr. Green has seen the dorsal artery arising from the obturator, which was given off from the femoral a little below Poupart's ligament. Cruveilhier has seen the dorsal artery of the penis arise from the superficial or external pudic, near the aperture for the saphena vein, and, after forming a curvature in the groin, with its convexity turned downwards, proceed along the lateral surface of the penis. In another case, in addition to its usual root, which was diminutive, it had a second of considerable size, which arose from the obturator artery, and passed under the symphysis pubis, to join the former.
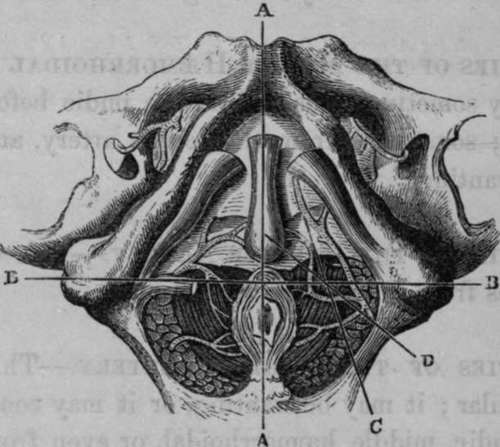
Fig. 73. Represents the Surgical Anatomy of the Male Perineum, the Artery of the Bulb arising farther back than usual, opposite the Tuber Ischii (after Maclise).
A, A, Median Line, intersecting B, B, dividing the Perineum into the Anterior and Posterior Regions. C, D, Lines showing the course of neisions which would divide the Artery of the Bulb in a case of this Abnormal Origin; or the Internal Pudic Artery in case the incision be carried too far outwards. An incision, which C represents, would also divide the Artery of the Bulb in its Normal Situation.
Varieties Of The Ilio Lumbar Artery
This vessel not unfrequently comes from the glutaeal: sometimes it is double,—its iliac and lumbar branches arising separately. Its size often seems to depend on the number of lumbar arteries; the ilio-lumbar being small whenever there happens to be a fifth lumbar artery.
Varieties Of The Lateral Sacral Artery
This artery sometimes arises from the ilio-lumbar, and frequently from the glutaeal. Occasionally, instead of forming an arch inferiorly, it terminates by entering the last sacral foramen.
Varieties Of The Middle Hemorrhoidal Artery
This artery sometimes comes from the pudic before it leaves the pelvis; sometimes from the sciatic artery, and occasionally it is wanting.
Varieties Of The Uterine Artery
This vessel sometimes arises from the internal pudic.
Varieties Of The Vaginal Artery
This artery is very irregular; it may be wanting, or it may come from the uterine, pudic, middle haemorrhoidal, or even from the obturator.
Varieties Of The Epigastric Artery
This artery may arise higher up than usual; or it may arise in common with the obturator, or from the upper part of the femoral, or from the profunda femoris.
Varieties Of The Circumflexa Ilii Artery
This vessel is sometimes double. It may arise from the femoral or from the epigastric.
Continue to:
