The External Plantar Artery
Description
This section is from the book "Anatomy Of The Arteries Of The Human Body", by John Hatch Power. Also available from Amazon: Anatomy of the Arteries of the Human Body, with the Descriptive Anatomy of the Heart.
The External Plantar Artery
The External Plantar Artery, much larger than the preceding, passes obliquely forwards and outwards towards the base of the fifth metatarsal bone: in this the first part of its course, it nearly follows the outer margin of the flexor digitorum communis, having above it the accessory muscle, and beneath it the plantar fascia and short flexor of the toes. In the second part of its course it lies deeper, and passes forwards between the flexor brevis and the abductor minimi digiti, and then turns inwards through a triangular space, bounded in front by the transversalis pedis, posteriorly and internally by the adductor of the great toe, and externally by the short flexor of the little toe; the interosseous muscles lie above it, and the common flexor tendons beneath it: its corresponding nerve crosses to its inside, the artery being superficial at the crossing. Finally, the external plantar terminates by becoming continuous with the communicating branch of the anterior tibial between the metatarsal bones of the first or great toe and of that next to it, thus completing the plantar arch of arteries. From this account, it follows that the artery is deeply seated, and describes in its entire course a curvature, the convexity of which looks forwards and outwards : it is also curved to accommodate itself to the lateral and antero-posterior arches of the foot. In the foetus and young subject, the ossification of the tarsal and metatarsal bones not being completed, these arches of the foot do not exist, and the artery consequently lies nearer to the integuments.
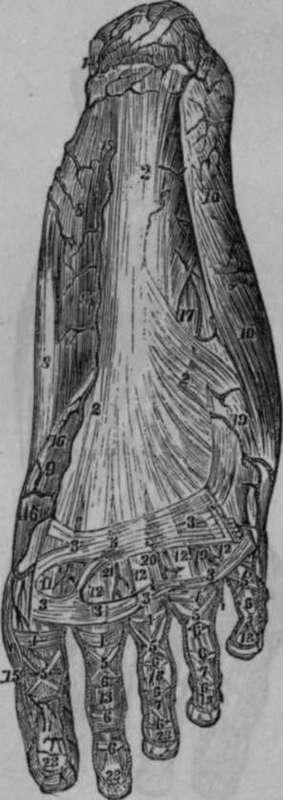
Fig. 69. Represents the Superficial Arteries of the Sole of the Foot in an adult.
2, 2, 2, The Plantar Aponeurosis. 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, Transverse bands connecting the anterior divisions of Plantar Aponeurosis. 4, 4, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 7, 7, 7, Ligaments of the Plantar Aspect of the Toes. 8, 8, Abductor Pollicis Muscle. 9, Portion of the Plexor Pollicis Brevis Muscle. 10, 10, Abductor Minimi Digiti Muscle. 11, 11, Tendon of the Flexor Pollicis Longus. 12, 12, 12, 12, Tendons of the Short Flexor of the Toes. 13, 13, 13, 13, Tendons of the Long Flexor of the Toes. 14, 14, Arterial Anastomosis on the Calcis. 15, 15, Internal Plantar Artery. 16, 16, Internal Digital Artery of the Great Toe. 17, External Plantar Artery. 18, First or External Digital Artery or Little Toe. 19, Second Digital Artery. 20, Third Digital Artery. 21, Fourth Digital Artery. 22, Fifth Digital Artery. 23, 23, 23, Arches formed by the Anastomosis of the Digital Arteries.
The branches of the external plantar artery may be classed into three sets, viz.:—
Superior or Perforating; Posterior and Inferior, or Muscular; and the Anterior or Digital.
The Superior Or Perforating Branches
The Superior Or Perforating Branches ascend between the metatarsal bones, and anastomose with the interosseous branches of the metatarsal artery.

Fig. 70. Represents the distribution of the Arteries of the Sole of the Foot. The Plantar Aponeurosis and the Short Flexor of the Toes have been removed.
1, Origin of the Short Flexor of the Toes, cut. 2, 2, 2, 2, Tendons of the preceding Muscle. 3, 3, Abductor Pollicis Muscle. 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, Tendons of the Long Flexor of the Toes. 5, 6, Accessory Muscle. 6, 6, Tendon of the Flexor Pollicis Longus.
7, 7, 7, 7, The Lumbricales. 8, Portion of the Short Flexor of the Little Toe. 9, 9, 10, Abductor Minimi Digiti. 11, Posterior Tibial Artery. 12, Branch to Calcis from preceding Artery. 13, Branch to Calcis from Posterior Peroneal Artery. 14, Internal Plantar Artery. 15, Sixth Digital Artery or Branch to the inner side of Great Toe from the Dorsalis Pollicis. 16, External Plantar Artery. 17, First Digital Artery running along the outside of Little Toe. 18, Second Digital Artery. 19, Perforating Twig from the preceding Artery. 20, 21, 22, Third, Fourth, and Fifth Digital Arteries. 23, Dorsal Twigs of Great Toe.
The Posterior And Inferior, Or Muscular Branches
The Posterior And Inferior, Or Muscular Branches, are distributed to the interosseous muscles and lumbricales, and to the tarso-metatarsal articulations.
Continue to:
