Inferior Turbinate Bone
Description
This section is from the book "The Anatomy Of The Human Skeleton", by J. Ernest Frazer. Also available from Amazon: The anatomy of the human skeleton.
Inferior Turbinate Bone
A bone projecting into the nasal cavity, attached to the maxilla and the other bones on the outer wall of the nose. It is covered by mucous membrane on both sides, and has its concave aspect looking toward the outer wall of the nose, and its convexity directed towards the septum.
It has :-(a) A lower or free border, thick and roughened by the vascular erectile tissue that covers it.
(b) A rounded anterior end, thick and covered by mucous membrane, which in the recent state is turned down off its front edge to form (Fig. 194) a fold passing towards the floor of the cavity.
(c) A pointed posterior end, lying against the vertical plate of the palate.
(d) An upper edge, by which it is attached. Connected with this border are three processes, ethmoidal, lachrymal, and maxillary ; the two first are directed upwards, but the maxillary process is turned down to fit into the lower part of the opening of the antrum. In front of the lachrymal process the bone articulates with the maxilla below the base of the nasal process ; the lachrymal process lies behind the nasal process and extends up to meet the lachrymal bone here, and, behind this, is in contact with the uncinate process of the ethmoid. The ethmoidal and maxillary processes form a plate which fits into the lower part of the antral opening, so that the edge of the maxillary part articulates with the lower border of the foramen while the upper projection stands up in the opening to join the end of the uncinate process. The upper edge, behind this " plate," is attached across the vertical plate of the palate. These various articulations can be seen in Figs. 191 and 194, 3.
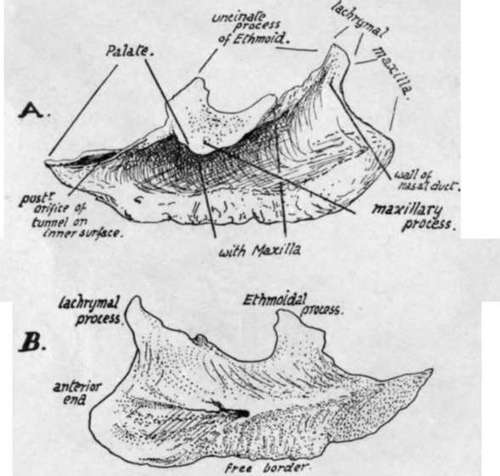
Fig. 191.-Right inferior turbinate bone, A. outer side, and B. inner or septal surface. To tell left from right, hold the bone with the pointed end behind, the thick roughened edge down, and the concavity externally.
(e) A deeply-concave outer surface, widest in front, where it is also smoother ; this part, just below the lachrymal process, forms the outer boundary of the lower portion and opening of the nasal duct.
(f) A convex and rough inner surface. A ridge in the posterior half, about midway up the bone, marks the position of a canal that carries a nerve and vessels from the posterior palatine set along the bone toward its front end.
Development
In the early foetus the lower edge of the nasal capsule, turned in, makes the projection of the lower turbinal : a centre appears on the surface of this cartilage in the fifth or sixth month or later and extends quickly. The bone frequently joins the ethmoid before middle life.
Continue to:
- prev: Vomer
- Table of Contents
- next: Nasal Bone
